The AI revolution isn't about to happen; it's happening right now.
Millions of people worldwide are interacting with these intelligent machines and technologies, and who knows where this new tech will lead us?
But what's the current level of interest in the different types of AI generation tech? That question inspired this latest study from the researchers at Electronics Hub. They analyzed Google search data to find out what countries are searching for text, voice, audio, and image bots the most.
Here's what they found out.
But first, let's start with a brief look at the past, present, and future of AI generation.
The emergence of machine learning techniques in the late 1990s and early 2000s revolutionized the development of AI-generative tools. Algorithms could learn from data, recognize patterns, and generate outputs not explicitly programmed by human developers.
In the 2010s, deep learning architectures like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) took the capabilities of generative tools even further, allowing systems to create more realistic and complex content, including images, music, and text.
GANs lay the groundwork for the most sophisticated AI tools we've ever seen, such as OpenAI's GPT models. They can replicate human text and content with increasing sophistication. Chat GPT is now smart enough to write grade-A high school papers and ace the bar exam.
However, critics argue that these systems still lack the depth of understanding, intuition, and emotional resonance that human artists and writers possess.
AI tools may be able to replicate patterns and structures. Still, the unique insights, cultural contexts, and personal expressions that humans bring to their work may be far more challenging to emulate. The consensus seems that while AI generative tools are improving, they have not yet reached true human-like creativity in writing or drawing.
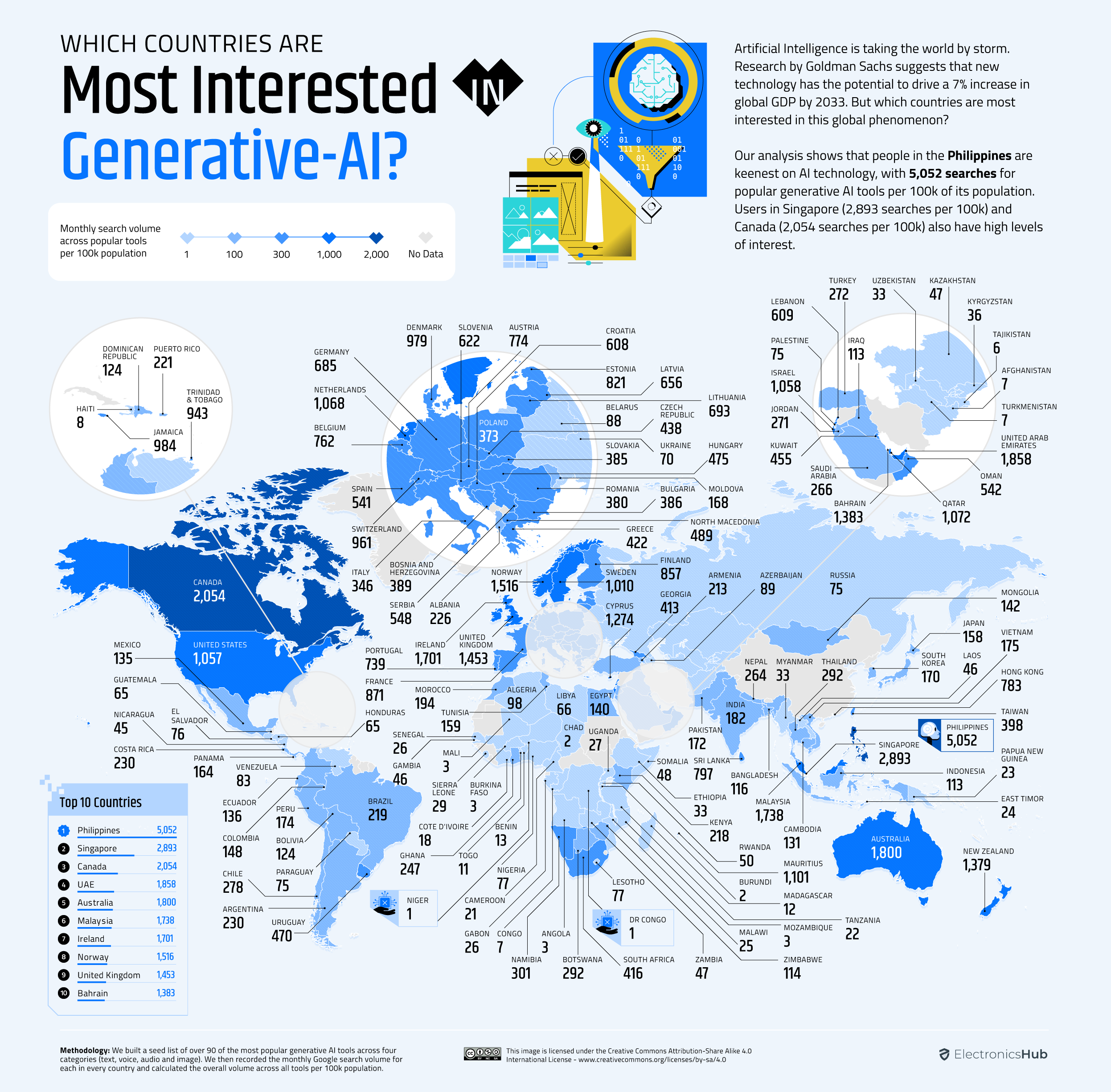
According to the Electronics Hub research, The Philippines has the highest monthly search volume for AI. 5,052 per 100,000 people in the Philippines are actively searching and researching topics related to AI and text AI tools.
Universities and research institutions in Israel are actively engaged in AI research, contributing to the global knowledge base. Israel's emphasis on technological innovation and entrepreneurship has made it a significant player in the global AI landscape.
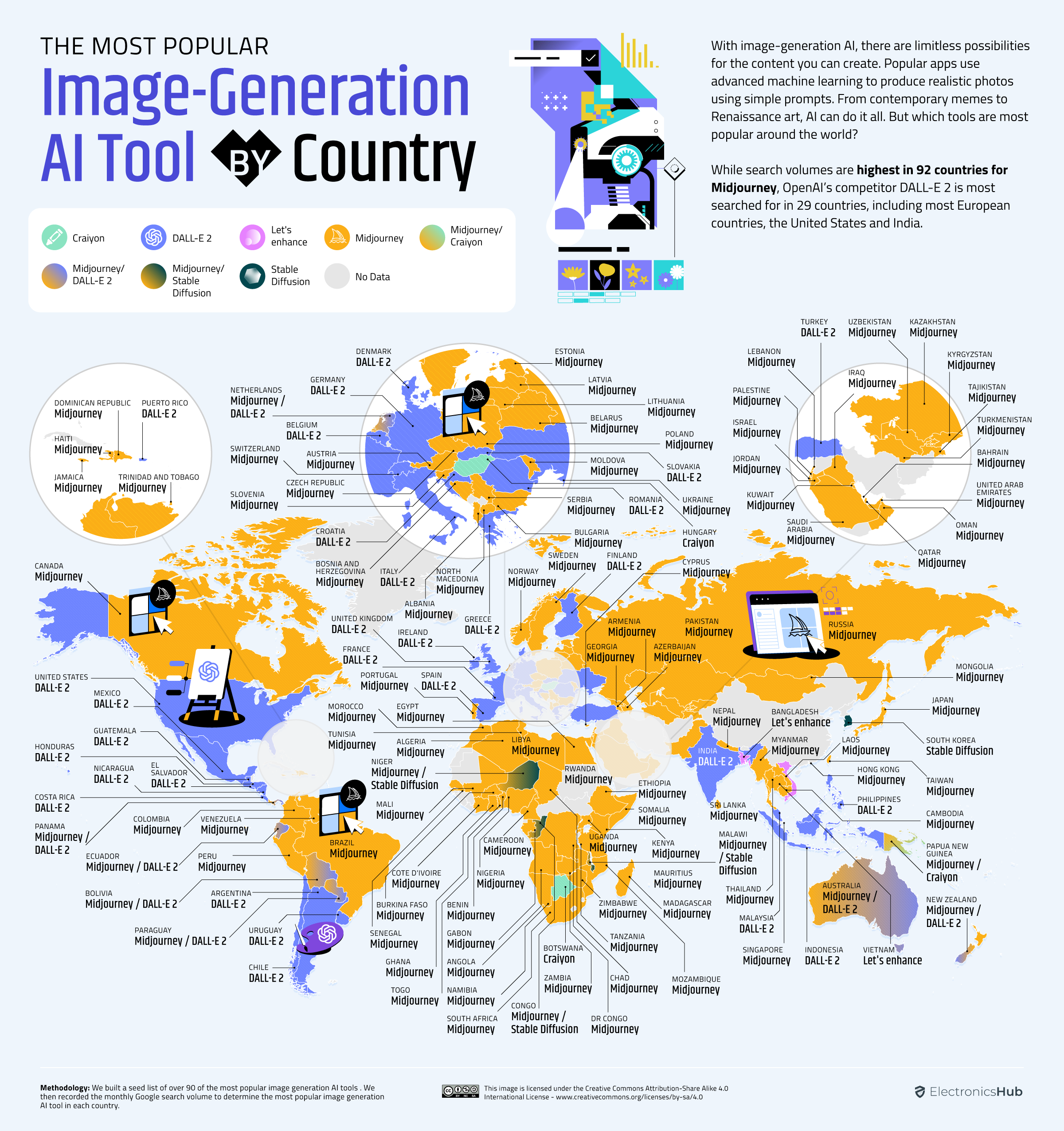
And this intense focus on AI is filtering down to the general population, especially regarding interest in AI image-generating tools like Midway. Electronics Hub discovered that 305 out of every 100,000 people in Israel are using or researching AI-generating tools regularly.
What happens when it can replicate anyone's voice? The implications are Terminator-level terrifying. It’s something that South Americans seem extremely concerned about. The study shows that searches for this type of technology are most popular across the continent of South America, but especially in Uruguay.
AI video generation tools utilize advanced algorithms to create or modify video content. These tools can generate realistic scenes, animate characters, or enhance video quality. While innovative and efficient, they also raise concerns about authenticity and potential misuse, such as creating deep fake videos that convincingly replace a person's likeness and voice.
Earlier this year, scammers used an AI-generated video of money-saving expert Martin Lewis to trick people into putting their cash into a fake Elon Musk-back investment scheme.
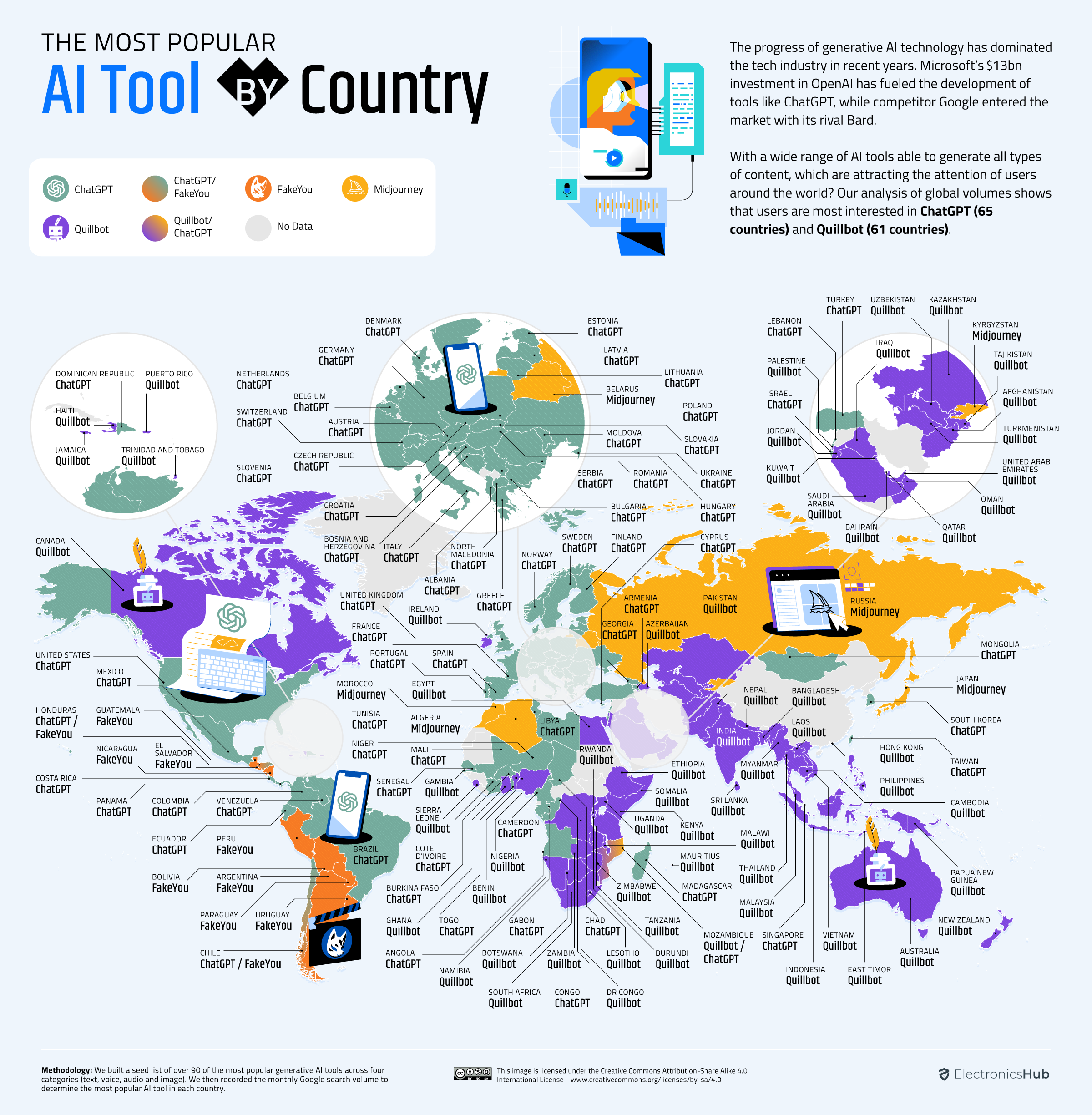
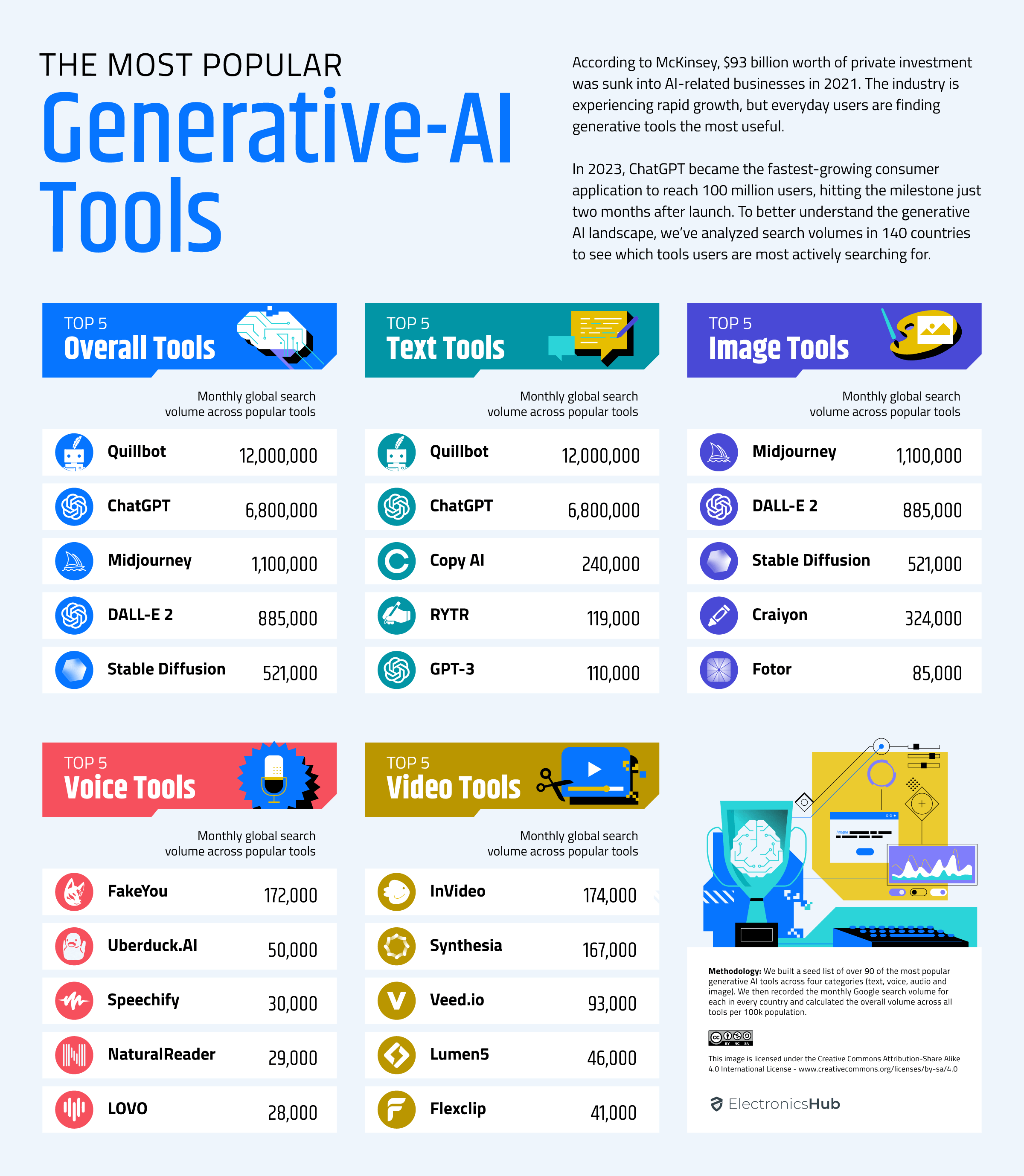
ChatGPT is the most popular and by quite some distance.
But Quillbot is gaining significant traction, especially in non-English speaking regions. This is probably due to its fluent rewriting feature, which can translate pasted text into over 20 languages.
Millions of people worldwide are interacting with these intelligent machines and technologies, and who knows where this new tech will lead us?
But what's the current level of interest in the different types of AI generation tech? That question inspired this latest study from the researchers at Electronics Hub. They analyzed Google search data to find out what countries are searching for text, voice, audio, and image bots the most.
Here's what they found out.
But first, let's start with a brief look at the past, present, and future of AI generation.
A brief history of AI generative tools
Early AI systems were based on rule-based algorithms and fixed patterns, often mimicking the human capacity for decision-making and problem-solving. However, they were limited in their creativity and ability to generate new content.The emergence of machine learning techniques in the late 1990s and early 2000s revolutionized the development of AI-generative tools. Algorithms could learn from data, recognize patterns, and generate outputs not explicitly programmed by human developers.
In the 2010s, deep learning architectures like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) took the capabilities of generative tools even further, allowing systems to create more realistic and complex content, including images, music, and text.
GANs lay the groundwork for the most sophisticated AI tools we've ever seen, such as OpenAI's GPT models. They can replicate human text and content with increasing sophistication. Chat GPT is now smart enough to write grade-A high school papers and ace the bar exam.
Will AI ever be as creative as humans?
Advancements in AI technologies, particularly in deep learning and neural networks, have enabled machines to generate increasingly complex and nuanced content. Models such as GPT-3 have demonstrated capabilities in producing human-like text, while AI-powered drawing tools can mimic certain artistic styles.However, critics argue that these systems still lack the depth of understanding, intuition, and emotional resonance that human artists and writers possess.
AI tools may be able to replicate patterns and structures. Still, the unique insights, cultural contexts, and personal expressions that humans bring to their work may be far more challenging to emulate. The consensus seems that while AI generative tools are improving, they have not yet reached true human-like creativity in writing or drawing.
What country is most interested in generative text AI?
Singapore is a global hub for innovations and tech adoption. So it's no surprise that the city-state is one of the biggest users of text-based AI generative tools like ChatGPT.According to the Electronics Hub research, The Philippines has the highest monthly search volume for AI. 5,052 per 100,000 people in the Philippines are actively searching and researching topics related to AI and text AI tools.
What country is most interested in image-generation AI?
AI adoption in Israel is evolving rapidly, reflecting the country's position as a hub for technological innovation. Government initiatives, alongside a thriving startup ecosystem, have facilitated the development and integration of AI across various sectors, including healthcare, defense, finance, and agriculture.Universities and research institutions in Israel are actively engaged in AI research, contributing to the global knowledge base. Israel's emphasis on technological innovation and entrepreneurship has made it a significant player in the global AI landscape.
And this intense focus on AI is filtering down to the general population, especially regarding interest in AI image-generating tools like Midway. Electronics Hub discovered that 305 out of every 100,000 people in Israel are using or researching AI-generating tools regularly.
Nations most interested in voice-generated AI
Fakeyou and Voicegpt can create highly convincing forgeries of individuals' voices from just a few snippets. It's a tool that's ripe for fraudulent activities or manipulation of information and has already been central in several online scams where fake versions of famous people advertised products or services that don't actually exist.What happens when it can replicate anyone's voice? The implications are Terminator-level terrifying. It’s something that South Americans seem extremely concerned about. The study shows that searches for this type of technology are most popular across the continent of South America, but especially in Uruguay.
What countries search for AI video generation tools the most?
Singapore makes another appearance here. 54 out of 100K people in Singapore are searching for information or content on AI video generation platforms.AI video generation tools utilize advanced algorithms to create or modify video content. These tools can generate realistic scenes, animate characters, or enhance video quality. While innovative and efficient, they also raise concerns about authenticity and potential misuse, such as creating deep fake videos that convincingly replace a person's likeness and voice.
Earlier this year, scammers used an AI-generated video of money-saving expert Martin Lewis to trick people into putting their cash into a fake Elon Musk-back investment scheme.
Global interest in AI-generation
Text tools, including AI-driven solutions, are gaining widespread popularity in 129 countries worldwide, owing to their effectiveness and broad applicability across various linguistic and cultural contexts.ChatGPT is the most popular and by quite some distance.
But Quillbot is gaining significant traction, especially in non-English speaking regions. This is probably due to its fluent rewriting feature, which can translate pasted text into over 20 languages.